UNDERSTANDING HOS REGULATIONS
Hours of Service (HOS) regulations are critical components of the trucking industry, designed primarily to ensure the safety of drivers and other road users by preventing fatigue-related accidents. These rules, enforced by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA), dictate how long drivers are allowed to operate and when they must rest.
Compliance with HOS regulations is not just a legal obligation—it also has significant implications for the operational efficiency and safety reputation of trucking companies. Mismanagement of HOS can lead to severe penalties, including fines, lowered safety ratings, and increased insurance premiums.
The objective of this article is to provide a comprehensive overview of how HOS regulations impact trucking operations. We will explore the specific rules and their operational implications, discuss recent changes and exceptions, and offer strategies to manage compliance effectively while maintaining operational efficiency. By understanding and navigating these regulations wisely, trucking companies can optimize their operations, ensure safety, and improve their bottom line.
THE BASICS OF HOS REGULATIONS
Core Rules
Hours of Service regulations are designed to limit the amount of time drivers can be on duty and driving, to ensure they have sufficient rest. The key components include:
- 14-hour driving window: Drivers have a window of 14 consecutive hours in which they can drive up to 11 hours after being off duty for 10 or more consecutive hours.
- 11-hour driving limit: Within the 14-hour window, drivers can drive for up to 11 total hours.
- 30-minute breaks: Drivers must take a 30-minute break if more than 8 hours have passed since their last off-duty or sleeper berth period.
- 60/70-hour limit: Drivers must not drive after 60/70 hours on duty in 7/8 consecutive days. A reset can occur after 34 consecutive hours of rest.
Recent Changes
Recent updates to HOS regulations include modifications to the sleeper berth provision, allowing drivers to split their required 10 hours off duty into two periods, provided one period is at least 7 consecutive hours in the sleeper berth. The other period must be at least 2 hours long, either off duty or in the sleeper berth, without extending the 14-hour window.
Exemptions and Special Cases
There are several exemptions to the standard HOS rules:
- Adverse driving conditions: Drivers can extend the 11-hour maximum driving limit and 14-hour driving window by up to 2 hours when adverse driving conditions are encountered.
- Short-haul exemption: Drivers operating within a 150-air-mile radius of their work reporting location and who return to the same location within 12 hours may be exempt from maintaining logs and using Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs).
- Agricultural exemptions: During certain times of the year, drivers transporting agricultural commodities within a 150-air-mile radius from the source of the commodities are exempt from HOS regulations.
OPERATIONAL IMPACTS OF HOS
Scheduling Challenges
HOS regulations significantly influence how dispatchers and fleet managers schedule drivers. The strict limits on driving hours mean that meticulous planning is essential to maximize efficiency while remaining compliant. For example, unexpected delays such as traffic or weather can disrupt planned routes and require rapid adjustments to ensure drivers do not exceed their legal driving hours.
Driver Utilization
Effectively managing driver utilization is crucial under HOS rules. Since drivers are limited in how long they can operate daily and weekly, optimizing their schedules to get the most out of available driving hours is key. This involves strategic planning of routes and loads to avoid leaving drivers idle or wasting available hours, thereby improving overall operational efficiency.
Impact on Delivery Timelines
HOS regulations directly affect delivery schedules. Companies must account for mandated rest periods and driving limits when planning delivery timelines. This can sometimes lead to longer transit times, especially for long-haul deliveries. To mitigate these effects, companies often need to adjust customer expectations or explore strategies like using team driving, where two drivers alternate shifts to keep the truck moving more continuously.
COMPLIANCE STRATEGIES FOR HOS
Training and Education
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Essential for both new and experienced drivers, these programs should cover the specifics of HOS regulations, the use of Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs), and the importance of compliance. Regular refresher courses can help keep these crucial details top of mind.
- Dispatcher and Manager Training: Equally important is the training of dispatchers and managers who plan routes and schedules. They must understand HOS rules to effectively manage compliance across their operations.
Technology Solutions
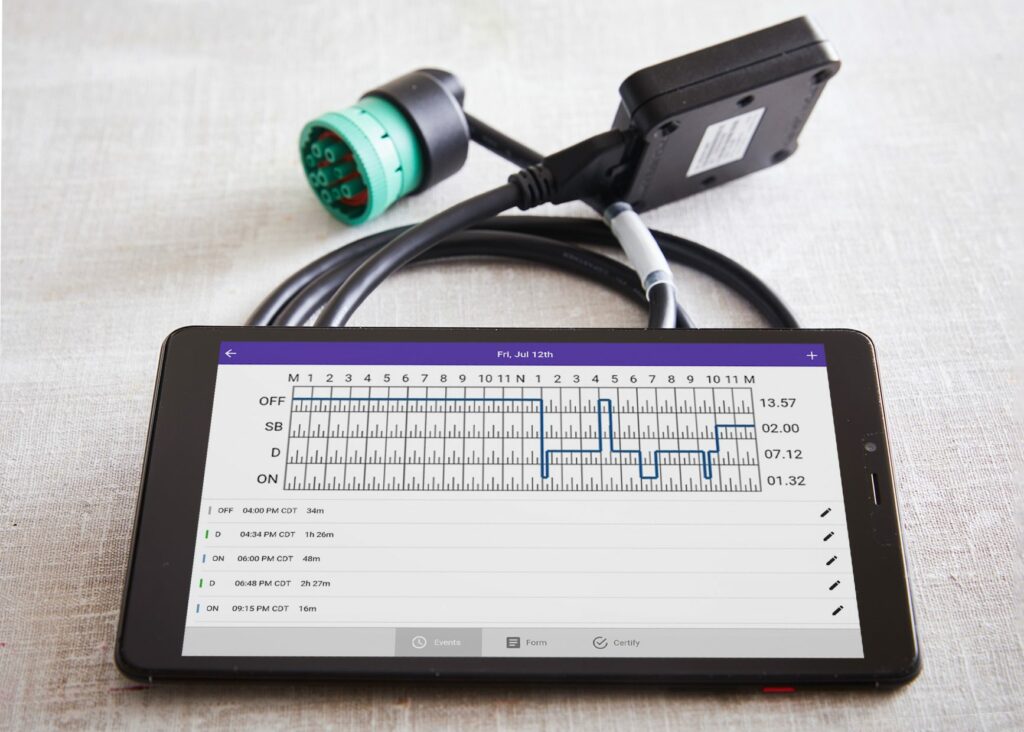
- Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs): Mandatory for most commercial drivers, ELDs automatically record driving time and hours of service, ensuring accurate tracking and easier compliance with HOS regulations.
- Software for Route and Schedule Optimization: Advanced software can help plan the most efficient routes and schedules, taking into account HOS regulations and other constraints, thus maximizing driver utilization without breaching regulations.
Record Keeping and Audits
Maintaining Accurate Records: Beyond using ELDs, companies should maintain organized and accessible records of hours of service logs and other relevant documentation.
- Preparing for Audits: Regular internal audits of HOS records can help identify and correct discrepancies before they lead to violations. Training on how to handle DOT inspections can also prepare drivers and staff to navigate these checks smoothly.
ENHANCING EFFICIENCY WITHIN HOS CONSTRAINTS
Route Optimization Tools
- Utilizing GPS and Routing Software: These tools help plan the most efficient routes that take into account not only distance and traffic but also HOS restrictions. By optimizing routes, companies can ensure that drivers utilize their available hours in the most productive manner possible.
- Real-time Traffic Updates: Incorporating real-time traffic data can prevent unexpected delays by rerouting drivers around traffic jams or accidents, thereby maintaining compliance with HOS.
Flexible Scheduling Practices
- Adjustable Shifts and Rotations: Implementing flexible scheduling allows for adjustments based on real-world conditions and driver preferences, which can lead to more efficient use of available hours.
- Team Driving Options: For long-haul routes, using team drivers can effectively double the available driving hours, ensuring that trucks can continue moving while complying with HOS regulations.
Driver Health and Morale
- Regular Breaks and Rest Periods: Ensuring that drivers take adequate breaks not only complies with HOS but can also improve driver alertness and reduce the risk of accidents.
- Support for Health and Wellness: Programs aimed at supporting driver health, such as ergonomic assessments and access to fitness facilities, can improve overall driver well-being, leading to better performance and satisfaction.
NAVIGATING HOS FOR BETTER TRUCKING OPERATIONS

Navigating the Hours of Service (HOS) regulations effectively is not merely about compliance; it’s about integrating these rules into the fabric of daily operations to enhance safety, efficiency, and profitability. This article has explored various dimensions of HOS regulations and their impact on the trucking industry, providing practical strategies to manage and optimize these regulations within trucking operations.
Summary of Key Strategies:
-
Understanding the Basics: Comprehensive knowledge of HOS regulations is crucial for both drivers and management to ensure all operations remain within legal bounds.
-
Operational Impacts and Management: Adapting operations to accommodate HOS regulations can prevent costly violations and enhance route efficiency.
-
Compliance Strategies: Leveraging technology like ELDs and optimizing routes and schedules ensures compliance while maximizing operational efficiency.
-
Efficiency Enhancements: Implementing flexible scheduling and focusing on driver health and morale can improve job satisfaction and productivity, within the limits set by HOS regulations.
Call to Action: Trucking companies are encouraged to continuously evaluate and adapt their HOS strategies. Embracing innovative technologies and practices not only aids in compliance but also boosts overall operational effectiveness. Staying ahead of regulatory changes and industry trends will be key to maintaining competitive advantage and operational resilience.
Looking Ahead: As the trucking industry evolves, so too will the regulations that govern it. Companies that proactively engage with these changes and integrate flexible, tech-driven solutions will be best positioned to thrive. Continued investment in driver training, technology, and wellness programs will remain essential components of successful HOS management.